Java Stream API — Even Numbers (Full Screen) Java Stream API — Get Even Numbers Example 1 — Filter even numbers from a list Creates a list, uses Stream to filter evens, and prints them. Copy import java.util.*; import java.util.stream.*; public class EvenNumbersStream { public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a list of numbers List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10); // Use Stream API to filter even numbers List<Integer> evenNumbers = numbers.stream() .filter(n -> n % 2 == 0) .collect(Collectors.toList()); // Print the even numbers System.out.println( "Even numbers: " + evenNumbers); } } Example 2 — Use IntStream.rangeClosed ...
Write a C program to find the root of equation using Newton Raphson Method. Equation: 2x^3-6x^2+6x-1
In this C program we will find the root of equation using Newton Raphson Method. The equation is: 2x^3-6x^2+6x-1
The allowed error is: 0.001
Introduction:
Introduction:From NewtonRaphson Method we know, Xn+1=Xn-[f(x)/f'(x)].Here we consider three functions one to generate the given equation, other to generate the derivative of the given equation. And the other to find out the root of the equation by using Newton Raphson Method. For this here we passes two values given by the users.
input:
a and b, two arbitrary values will be given by the user.output:
The root of the equation.
CODE---->
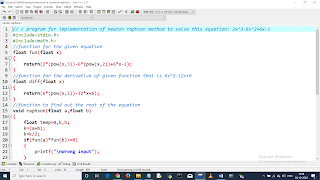
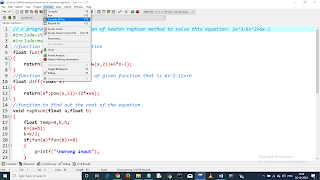
// c program for implementation of newton raphson method to solve this equation: 2x^3-6x^2+6x-1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
//function for the given equation
float fun(float x)
{
return(2*(pow(x,3))-6*(pow(x,2))+6*x-1);
}
//function for the derivative of given function that is 6x^2-12x+6
float diff(float x)
{
return(6*(pow(x,2))-12*x+6);
}
//function to find out the root of the equation
void raphson(float a,float b)
{
float temp=0,k,h;
k=(a+b);
k=k/2;
if(fun(a)*fun(b)>=0)
{
printf("\nWrong input");
}
else
{
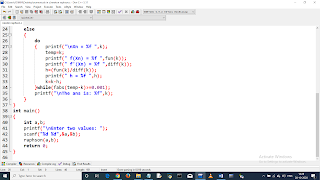
do
{ printf("\nXn = %f ",k);
temp=k;
printf(" f(Xn) = %f ",fun(k));
printf(" f'(Xn) = %f ",diff(k));
h=(fun(k)/diff(k));
printf(" h = %f ",h);
k=k-h;
}while(fabs(temp-k)>=0.001);
printf("\nThe ans is: %f",k);
}
}
int main()
{
int a,b;
printf("\nEnter two values: ");
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
raphson(a,b);
return 0;
}
Download the C-Program file of this Program.
Download the MS-Word file of this whole assignment with algorithm.
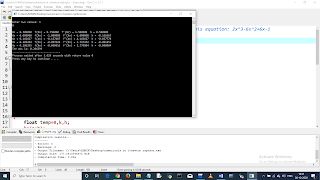
RESULT :
Enter two values: 1 0 Xn = 0.500000 f(Xn) = 0.750000 f'(Xn) = 1.500000 h = 0.500000 Xn = 0.000000 f(Xn) = -1.000000 f'(Xn) = 6.000000 h = -0.166667 Xn = 0.166667 f(Xn) = -0.157407 f'(Xn) = 4.166667 h = -0.037778 Xn = 0.204444 f(Xn) = -0.007028 f'(Xn) = 3.797452 h = -0.001851 Xn = 0.206295 f(Xn) = -0.000016 f'(Xn) = 3.779804 h = -0.000004 The ans is: 0.206299 -------------------------------- Process exited after 6.369 seconds with return value 0 Press any key to continue . . .
Images for better understanding :

Comments
Post a Comment