Java Stream API — Even Numbers (Full Screen) Java Stream API — Get Even Numbers Example 1 — Filter even numbers from a list Creates a list, uses Stream to filter evens, and prints them. Copy import java.util.*; import java.util.stream.*; public class EvenNumbersStream { public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a list of numbers List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10); // Use Stream API to filter even numbers List<Integer> evenNumbers = numbers.stream() .filter(n -> n % 2 == 0) .collect(Collectors.toList()); // Print the even numbers System.out.println( "Even numbers: " + evenNumbers); } } Example 2 — Use IntStream.rangeClosed ...
In this C program we will calculate the Factorial of a number(integer) using RECURSION method and print the result, in the screen. The number(integer) will be taken from the user.
input:
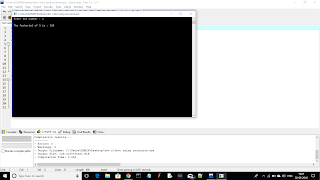
The number(integer) (i.e. 5,7 etc.)output:
The Factorial of the number will be printed on the screen.
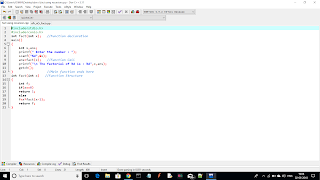
CODE---->
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int fact(int x); //Function declaration
main()
{
int x,ans;
printf(" Enter the number : ");
scanf("%d",&x);
ans=fact(x); //Function Call
printf("\n The factorial of %d is : %d",x,ans);
getch();
} //Main function ends here
int fact(int x) //Function Structure
{
int f;
if(x==0)
return 1;
else
f=x*fact(x-1);
return f;
}
Caution :
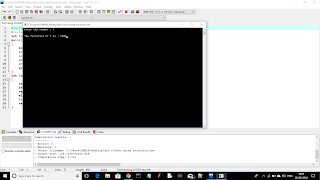
In this C-program we have used an integer number as an input and the variable where the calculated result is stored, is also an integer. The range of an integer variable is between -32,768 to 32,767, so, the calculation of a factorial must be in this range. otherwise, it will show you a garbage value or wrong calculation. You can prevent this problem by using "Long long signed integer type(%lli)". Capable of containing at least the [−9,223,372,036,854,775,807, +9,223,372,036,854,775,807] range.
But, this C-program is not a wrong Program.It's just about range.
RESULT:

Comments
Post a Comment